Can We Still Use Dental Floss?
Floss effectively removes plaque because it reaches the places toothbrushes don’t. It is a flagship accessory in terms of dental care. But given its finesse, we can also ask questions.
When To Use Dental Floss?
Dental floss aims to rid the interdental area (or “interproximal” in medical jargon) of food waste or dental plaque. Its use significantly impacts the protection of all teeth, especially against pathologies linked to poor oral hygiene and the proliferation of bacteria. Dental floss can be used on all days.
The community of stemmatologists prefers to recommend interdental brushes or other devices. On the other hand, this accessory is generally recommended for solid gums that are not prone to bleeding. Flossing is also not recommended for people with large interproximal areas who have had invasive procedures or suffer from periodontal disease.
How to use dental floss.
A simple method to contribute to the health of teeth, dental floss requires a few simple gestures:
The use of the wire is done before or after brushing the teeth, being an accessory
cut a good length (not less than 30cm) to facilitate movement
Gently insert the dental floss to avoid hurting the gums.
At the end of the cleaning, make the same back-and-forth movement by removing the thread
rinse the mouth well with water or a mouthwash solution
Choose Your Dental Floss Well.
The dental floss is designed in solid materials (nylon, PE, Teflon…) to prevent them from fraying or being cut quickly. But designers give them other features to meet various kinds of needs and preferences:
- waxed to facilitate passage between the teeth even more (untaxed, dental floss cleans more effectively)
- impregnated with antibacterial agents for antiseptic action
- flavored (with mint, for example) for a more pleasant use
Dental Floss
Dental floss can be presented as reels and forks… aiming to maximize its practicality. The user should nevertheless choose a thread that is neither too thin nor too thick so that it does not, against all odds, constitute another factor of toothache.
Brushing Your Teeth, The Right Things To Do
Daily tooth brushing is recommended to limit bacterial attacks and the formation of dental plaque. This will prevent cavities and other oral health problems. This daily gesture also helps keep your breath fresh throughout the day.

The Right Gestures For Brushing Your Teeth
Ideally, it would be best for you to brush your teeth after each meal. If you cannot do this at noon due to professional constraints, brush them at least in the morning after breakfast and in the evening before bed. At a minimum, each brushing should last three minutes.
The upper and lower teeth of the jaw should be cleaned separately. Brushing is done vertically, going from the gum to the tooth. Be careful not to forget to brush the inside and top of the teeth. Finally, to avoid damaging the enamel, brushing must be done gently.

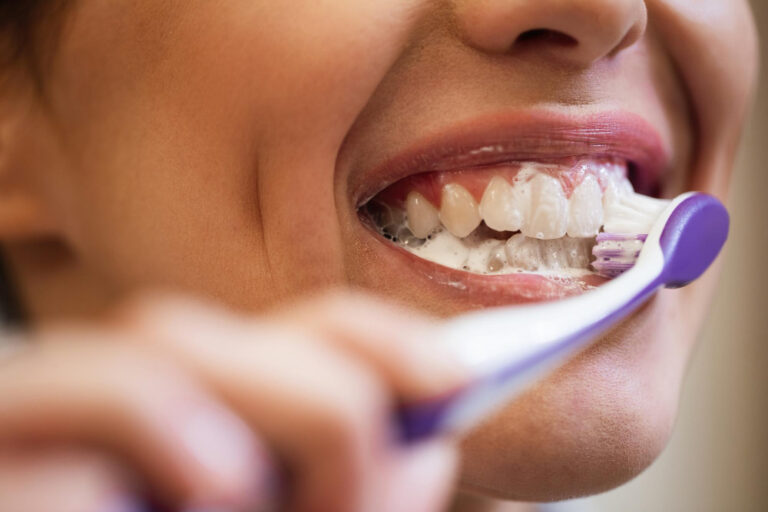
Good Equipment For Effective Brushing
As a material, ban toothbrushes with hard bristles, which are too aggressive for the gums. Prefer one with soft bristles. Small brushes have the advantage of sliding well everywhere and reaching the remote parts of the oral cavity. In any case, for comfortable use, it must be adapted to the individual’s age.
It is also essential to change your toothbrush every three months. Indeed, over time, it loses its effectiveness and accumulates microbes that may affect the hygiene of your teeth. Of course, we must not forget the toothpaste, which must be fluoride-free for toddlers. If your child wears braces, opt for the formulas dedicated to them. Also, do not hesitate to choose toothpaste with special tastes so that your children enjoy these times of the day more.
Finally, for impeccable hygiene, dental floss or interdental brushes should be used after each brushing to remove the last waste that has resisted the toothbrush.

Saliva
Saliva, the liquid that moistens the mucous membranes of the mouth, is secreted by the parotid, sublingual, submandibular salivary glands, and accessory glands under the mucous membrane. It comprises water (99%), proteins, electrolyte ions, mineral salts, digestive enzymes, and organic elements (1%). An adult produces an average of 1 liter per day. The flow is greater when standing and lying down, less when sitting, and minimal at night.
Saliva performs several functions. It facilitates diction by lubricating the mucous membranes’ surface and intervenes in food digestion. It also participates in maintaining the physiological balance of the oral cavity.
Saliva And Digestion
Saliva facilitates swallowing and prepares food for digestion. It moistens food during chewing to form a “food bolus.” Thus lubricated, the food slides easily toward the esophagus, which prevents us from choking.
It also participates in digestion by transforming specific food components by chemical reaction and thus facilitating their assimilation by the body.
Finally, saliva promotes the functioning of taste buds which only function in a humid environment. It is she who allows us to feel the taste of food.
Saliva As Protection
Saliva is also essential for maintaining the physiological balance of the oral cavity. It has antibacterial properties. It thus prevents the proliferation of undesirable microorganisms. It is a natural bulwark against microbial invasions.
Saturated with calcium and phosphate ions, saliva also prevents the corrosion of tooth enamel by creating a protective layer of molecules on their surfaces.
The Restorative Property Of Saliva
In addition to the functions mentioned above, saliva also plays a vital role by regulating the pH of our mouth after food intake. The fact is that after a meal, the mouth’s pH becomes acidic. Such an environment favors the development of bacteria responsible for cavities. The increase in salivary flow helps regulate this pH and reduces acid attacks. Even better, saliva demineralizes tooth enamel during this process and repairs the effects of acid attacks.
Be that as it may, the effectiveness of saliva remains limited. This is why the need to drink can be felt during meals, or good oral hygiene remains essential despite its antibacterial and therapeutic properties.
How To Avoid Having Sensitive Gums?
Sensitive gums are a problem often encountered in dental pathologies. This problem has several origins and also knows several solutions. So how do you take care of your gums to avoid pain?
Many solutions exist to limit, or even avoid, pain due to heat or cold and the sensitivity that one feels at the slightest contact with the gums.
Here are some answers to help you…
Brushing Your Teeth: A Moment To Take Care Of Your Gums
Brushing your teeth is often dreaded by people suffering from gum sensitivity. Indeed, contact with water (hot or cold), toothpaste, or the toothbrush can quickly become a source of pain. In this case, you may need to make a few changes:
— Toothbrush s: opt for a toothbrush with soft bristles. Avoid stiff bristles, which will attack the gums.
— Toothpaste: some toothpaste has the effect of desensitizing the gums. Check the packaging of the one you use. Otherwise, some brands offer, commercially or in pharmacies, desensitizing toothpaste.
— brushing: as far as possible, avoid brushing the gums too heavily. The skin of the gums can be very fragile, and brushing too hard will only aggravate the sensitivity and, by extension, the pain.
— Dental floss: if you are used to using dental floss, be very careful. Often the gums are abused when flossing.
— Mouthwash: mouthwash eliminates unwanted bacteria in the mouth, freshens the breath, prevents gingivitis, and treats sensitive gums.
A Visit To The Dentist Is Essential When Your Gums Are Very Sensitive
If, despite your efforts, nothing changes, make an appointment with your dentist. Indeed, the sensitivity of your gums may be due to a disease: gingivitis. Healthy gums are pale pink, have slight bumps, and do not bleed.
You may be worried about gum disease if your gums don’t look like this. But rest assured, gingivitis can be treated very well.
There Are Several Types Of Gingivitis:
— Simple gingivitis: the presence of inflammation in the gums. They are red and have edemas.
— Hypertrophic gingivitis: the volume of the gums increases considerably and can cover one or more teeth. When brushing, the gums are painful and bleed very often.
— ulcers-necrotic gingivitis: this type of gingivitis is scarce. They are triggered by great stress or result from a more severe illness. In this case, the gums are raw, bleed without brushing, and are particularly painful.
In any case, your dental surgeon is the ideal person to treat you. Please don’t hesitate to consult in case of doubt.
Sensitive or painful gums are not inevitable. There is no need to accept pain silently; take charge of it, and don’t be afraid to treat it. Teeth are a part of the body that needs to be taken care of.

